The 5 Key Similarities and Differences between DL, AI & ML
The world of technology is replete with acronyms and jargon that can be daunting to the uninitiated. At the forefront of these are DL, ML, and AI, short for Deep Learning, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence, respectively.
These technologies are gaining prominence due to their transformative potential across industries and sectors. From healthcare to finance, from entertainment to logistics, they are revolutionizing how we live, work, and play.
Deep Learning, Machine Learning, and Artificial Intelligence are interrelated technologies, each with its distinctive characteristics, capabilities, and applications. While they are often used interchangeably, they are not the same. This article aims to demystify these terms and delve into their intricacies, commonalities, and differences.
So, let's embark on this exciting journey of understanding these cutting-edge technologies that are reshaping our world.
Understanding DL (Deep Learning)
Deep Learning (DL) is a subset of machine learning based on artificial neural networks with multiple layers or "deep" networks.
- DL models learn from vast amounts of unstructured and semi-structured data.
- The depth of layers in DL signifies its ability to process different features and combine outputs for the final result.
- DL models automatically improve their performance as they encounter more data.
- DL's strength lies in learning patterns and representations from data, making it effective for image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition tasks.
Exploring ML (Machine Learning)
ML or Machine Learning is a field of computer science that enables computers to learn from data without explicit programming.
- Machine Learning algorithms learn from data without relying on predetermined equations.
- They often require structured data and can process numerical and categorical data.
- ML handles tasks like regression, classification, clustering, and anomaly detection.
- Subdivided into supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning.
- ML evolves and improves with exposure to more data.
- Valuable for predictive analytics, recommendation systems, and autonomous vehicles.
The World of AI (Artificial Intelligence)
AI or Artificial Intelligence is the overarching concept that encapsulates both Deep Learning and Machine Learning. AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. These processes include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding.
AI is a multidisciplinary field that integrates computer science, psychology, linguistics, philosophy, and neuroscience.
It has two main types:
1. Narrow AI - which is designed to perform a narrow task such as voice recognition
2. General AI -which can perform any intellectual task that a human being can
The power of AI lies in its potential to mimic human cognition and carry out tasks that usually require human intelligence.
From Siri and Alexa to autonomous vehicles and predictive analytics, AI is increasingly becoming part of our everyday lives.
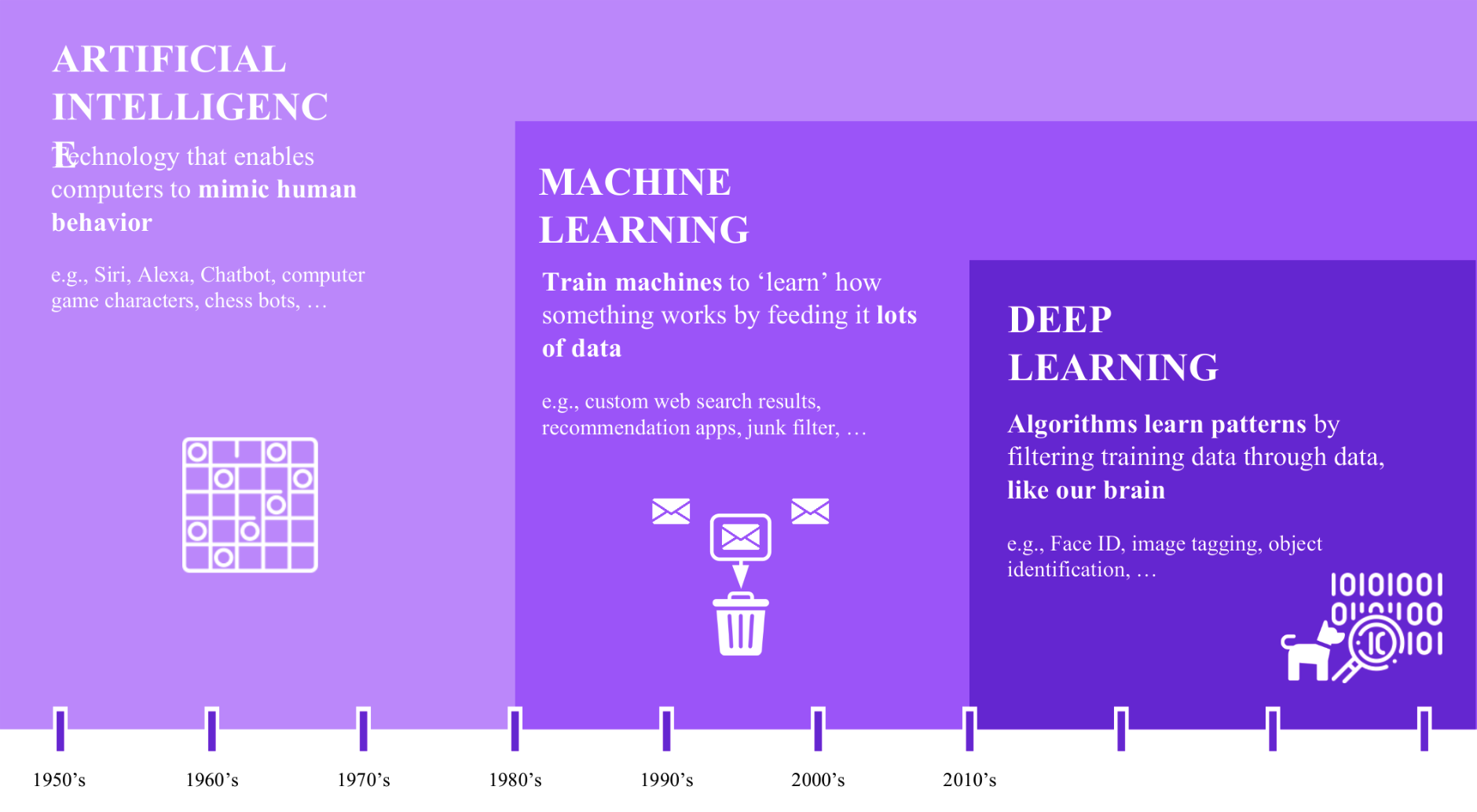
Comparing DL, ML, and AI: Key Similarities and Differences
- AI is a broad term encompassing smart computer programs, from complex tasks like beating chess champions to simple recommendations.
- Machine Learning is a subset of AI, teaching computers to learn from data.
- Deep Learning is a subset of Machine Learning, using sophisticated algorithms and neural networks for complex tasks like pattern recognition.
- AI provides the broad vision of mimicking human intelligence, ML provides methodologies and algorithms, and DL delves deeper into complex data interpretation structures.
The Role of DL in AI and ML
Deep Learning plays a significant role in both AI and ML. It's the engine that drives the most advanced applications of AI, including self-driving cars, voice-controlled assistants, and facial recognition systems.
In the context of Machine Learning, DL provides the deep neural networks that allow machines to process and understand complex patterns and correlations. In other words, if Machine Learning is the vehicle, Deep Learning is the engine that powers it.
Real-world Examples of DL, ML, and AI
Every day, we interact with applications powered by DL, ML, and AI. When we ask Siri a question, or when Netflix recommends a movie based on our viewing history, we're experiencing AI. When a self-driving car navigates through traffic, it's using a combination of AI and ML, with DL algorithms processing huge amounts of data from various sensors.
In healthcare, these technologies are helping to predict diseases, personalize treatment plans, and even assist in complex surgery. In finance, they're being used for credit scoring, algorithmic trading, and fraud detection.
Future Trends in DL, AI, and ML
The future of DL, AI, and ML is incredibly exciting. We're likely to see more integration of these technologies into our daily lives. From more sophisticated personal assistants to autonomous vehicles, the possibilities are endless.
On a larger scale, we can expect to see these technologies driving advancements in fields such as healthcare, finance, and climate science. They may even help us tackle some of the world's most significant challenges, such as curing diseases, reducing emissions, and managing resources more effectively.
Challenges and Opportunities in DL, ML, and AI
Despite their potential, DL, ML, and AI also present challenges. Issues such as data privacy, job displacement, and the ethical implications of AI are of significant concern. However, with careful regulation, clear ethical guidelines, and inclusive, human-centered design, we can mitigate these risks.
The opportunities these technologies present far outweigh the challenges. They have the potential not only to drive economic growth but also to improve quality of life, increase efficiency, and even tackle some of the world's most pressing problems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DL, ML, and AI are transformative technologies that are reshaping our world. While they may be complex and often misunderstood, their potential is vast. By understanding their intricacies and commonalities, we can better appreciate their impact and potential.
As we continue to navigate this exciting frontier, let's keep exploring, learning, and pushing the boundaries of what's possible with DL, ML, and AI. The journey is just beginning, and the future looks bright.
